BO - Wikilangs Models
Comprehensive Research Report & Full Ablation Study
This repository contains NLP models trained and evaluated by Wikilangs, specifically on BO Wikipedia data. We analyze tokenizers, n-gram models, Markov chains, vocabulary statistics, and word embeddings.
📋 Repository Contents
Models & Assets
- Tokenizers (8k, 16k, 32k, 64k)
- N-gram models (2, 3, 4-gram)
- Markov chains (context of 1, 2, 3 and 4)
- Subword N-gram and Markov chains
- Embeddings in various sizes and dimensions
- Language Vocabulary
- Language Statistics

Analysis and Evaluation
- 1. Tokenizer Evaluation
- 2. N-gram Model Evaluation
- 3. Markov Chain Evaluation
- 4. Vocabulary Analysis
- 5. Word Embeddings Evaluation
- 6. Summary & Recommendations
- Metrics Glossary
- Visualizations Index
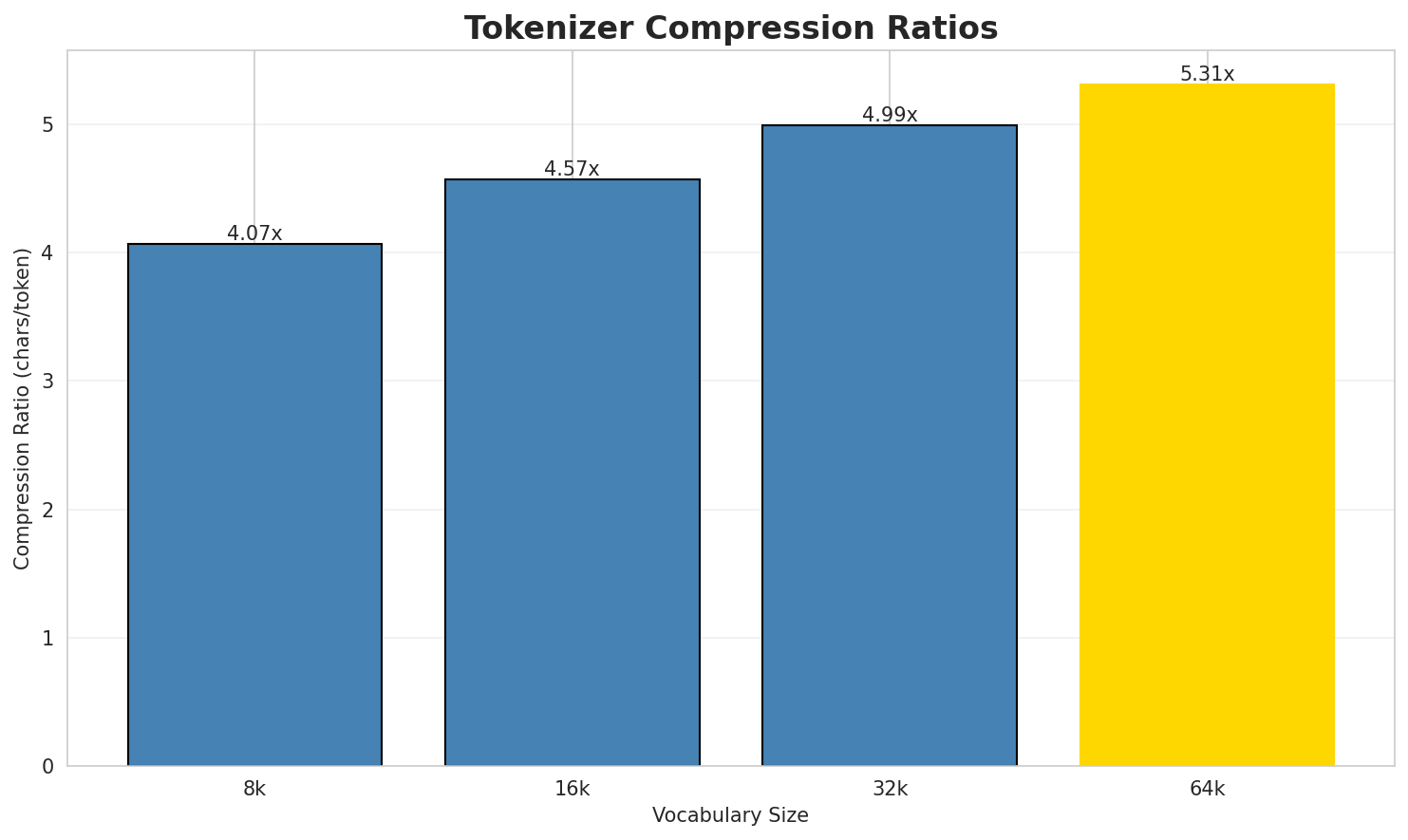
1. Tokenizer Evaluation
Results
| Vocab Size | Compression | Avg Token Len | UNK Rate | Total Tokens |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8k | 4.296x | 4.23 | 0.3002% | 389,363 |
| 16k | 4.846x | 4.77 | 0.3387% | 345,182 |
| 32k | 5.407x | 5.33 | 0.3779% | 309,326 |
| 64k | 5.961x 🏆 | 5.87 | 0.4166% | 280,591 |
Tokenization Examples
Below are sample sentences tokenized with each vocabulary size:
Sample 1: གསལ་བྱེད་སུམ་ཅུའི་ནང་ནས་ཀ་ག་བ་ཟ་ར་ས་དྲུག་ནི་ལ་བཏགས་ཅན་གྱི་ཡི་གེ་དྲུག་གོ། ༼དུང་དཀ...
| Vocab | Tokens | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 8k | ▁གས ལ་བྱེད་ སུམ་ ཅུའི་ ནང་ནས་ ཀ་ ག ་བ་ ཟ་ ར་ ... (+16 more) |
26 |
| 16k | ▁གསལ་བྱེད་ སུམ་ཅུའི་ ནང་ནས་ ཀ་ ག ་བ་ ཟ་ ར་ ས་ དྲུག་ ... (+13 more) |
23 |
| 32k | ▁གསལ་བྱེད་ སུམ་ཅུའི་ ནང་ནས་ ཀ་ ག་བ་ ཟ་ ར་ས་ དྲུག་ནི་ ལ་བཏགས་ ཅན་གྱི་ ... (+9 more) |
19 |
| 64k | ▁གསལ་བྱེད་ སུམ་ཅུའི་ ནང་ནས་ ཀ་ ག་བ་ ཟ་ ར་ས་ དྲུག་ནི་ ལ་བཏགས་ ཅན་གྱི་ ... (+9 more) |
19 |
Sample 2: བདག་སློབ་བུས་ལུས་ངག་ཡིད་གསུམ་ཁྱོད་ལ་དུས་བརྟན་དུ་འབུལ། ང་ཚོ་མྱུར་དུ་མཇལ་འཛོམ་ཡང...
| Vocab | Tokens | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 8k | ▁བདག་ སློབ་བ ུས་ ལུས་ ངག་ཡིད་ གསུམ་ ཁྱོད་ལ་ དུས་ བརྟན་ དུ་ ... (+18 more) |
28 |
| 16k | ▁བདག་ སློབ་བ ུས་ ལུས་ངག་ཡིད་ གསུམ་ ཁྱོད་ལ་ དུས་ བརྟན་ དུ་ འབུལ། ... (+13 more) |
23 |
| 32k | ▁བདག་ སློབ་བ ུས་ ལུས་ངག་ཡིད་གསུམ་ ཁྱོད་ལ་ དུས་ བརྟན་ དུ་ འབུལ། ▁ང་ཚོ་ ... (+12 more) |
22 |
| 64k | ▁བདག་ སློབ་བ ུས་ ལུས་ངག་ཡིད་གསུམ་ ཁྱོད་ལ་ དུས་ བརྟན་ དུ་ འབུལ། ▁ང་ཚོ་ ... (+10 more) |
20 |
Sample 3: མི་འཁྲུགས་པ་སྐྱབས་སྦྱིན་ཅན། དེང་སང་ཇོ་བོ་རིན་པོ་ཆེའི་སྐུ་རྒྱབ་ཏུ་བཞུགས་པའི་ཇོ...
| Vocab | Tokens | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 8k | ▁མི་ འཁྲུགས་ པ་ སྐྱབས་ སྦྱིན་ ཅན། ▁དེང་སང་ ཇོ་བོ་ རིན་པོ་ཆེའི་ སྐུ་ ... (+12 more) |
22 |
| 16k | ▁མི་ འཁྲུགས་ པ་ སྐྱབས་ སྦྱིན་ ཅན། ▁དེང་སང་ ཇོ་བོ་ རིན་པོ་ཆེའི་ སྐུ་ ... (+11 more) |
21 |
| 32k | ▁མི་ འཁྲུགས་པ་ སྐྱབས་ སྦྱིན་ ཅན། ▁དེང་སང་ ཇོ་བོ་ རིན་པོ་ཆེའི་ སྐུ་ རྒྱབ་ཏུ་བ ... (+7 more) |
17 |
| 64k | ▁མི་ འཁྲུགས་པ་ སྐྱབས་སྦྱིན་ ཅན། ▁དེང་སང་ ཇོ་བོ་ རིན་པོ་ཆེའི་སྐུ་ རྒྱབ་ཏུ་བ ཞུགས་པའི་ ཇོ་བོ་ ... (+5 more) |
15 |
Key Findings
- Best Compression: 64k achieves 5.961x compression
- Lowest UNK Rate: 8k with 0.3002% unknown tokens
- Trade-off: Larger vocabularies improve compression but increase model size
- Recommendation: 32k vocabulary provides optimal balance for production use
2. N-gram Model Evaluation
Results
| N-gram | Perplexity | Entropy | Unique N-grams | Top-100 Coverage | Top-1000 Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-gram | 397 🏆 | 8.63 | 16,730 | 60.3% | 96.5% |
| 2-gram | 259 🏆 | 8.02 | 10,716 | 68.5% | 98.4% |
| 3-gram | 2,660 | 11.38 | 107,789 | 28.7% | 70.8% |
| 3-gram | 1,576 | 10.62 | 61,755 | 31.0% | 81.3% |
| 4-gram | 14,448 | 13.82 | 410,390 | 13.4% | 41.2% |
| 4-gram | 7,647 | 12.90 | 237,121 | 14.5% | 47.5% |
Top 5 N-grams by Size
2-grams:
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ི ་ |
1,330,962 |
| 2 | ་ ས |
923,359 |
| 3 | ན ་ |
864,506 |
| 4 | ས ་ |
804,391 |
| 5 | ་ ར |
740,793 |
3-grams:
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ་ པ ་ |
412,050 |
| 2 | ྱ ི ་ |
279,592 |
| 3 | ོ ད ་ |
249,936 |
| 4 | ་ དང ་ |
232,586 |
| 5 | ་ ཀ ྱ |
225,678 |
4-grams:
| Rank | N-gram | Count |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ་ པའ ི ་ |
220,243 |
| 2 | ་ ཀ ྱ ི |
185,475 |
| 3 | ་ ར ྒ ྱ |
176,176 |
| 4 | ཀ ྱ ི ་ |
145,131 |
| 5 | ་ ད ུ ་ |
133,021 |
Key Findings
- Best Perplexity: 2-gram with 259
- Entropy Trend: Decreases with larger n-grams (more predictable)
- Coverage: Top-1000 patterns cover ~47% of corpus
- Recommendation: 4-gram or 5-gram for best predictive performance
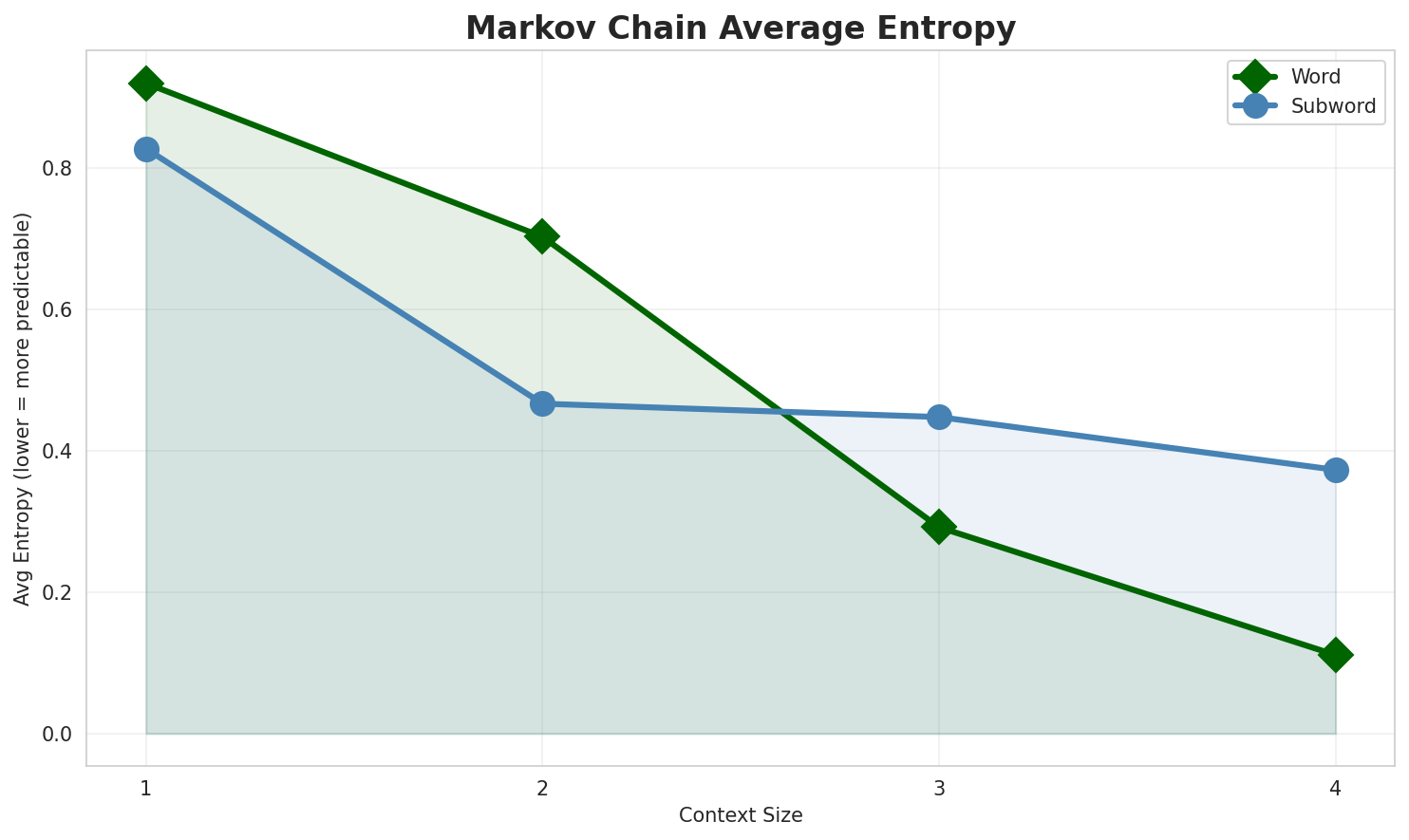
3. Markov Chain Evaluation
Results
| Context | Avg Entropy | Perplexity | Branching Factor | Unique Contexts | Predictability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.2954 | 1.227 | 3.27 | 41,503 | 70.5% |
| 1 | 1.4785 | 2.787 | 10.14 | 4,527 | 0.0% |
| 2 | 0.2647 🏆 | 1.201 | 2.76 | 135,576 | 73.5% |
| 2 | 0.6082 🏆 | 1.524 | 3.67 | 45,909 | 39.2% |
| 3 | 0.2919 | 1.224 | 2.37 | 373,945 | 70.8% |
| 3 | 0.5729 | 1.488 | 2.90 | 168,571 | 42.7% |
| 4 | 0.3575 | 1.281 | 2.36 | 884,085 | 64.2% |
| 4 | 0.4734 | 1.388 | 2.39 | 489,183 | 52.7% |
Generated Text Samples
Below are text samples generated from each Markov chain model:
Context Size 1:
་ བ ། ཉམས ་ ན ་ འག ྲ ག ་ མ ་ ཤ ུ ངི ར ྐ ྱ ན ་ བས ྒ ྲ ི ་ ད ་ མ ་ གཅོ ས ྙ ི ་ དང ་ ས ྲ ི ས ་ ཆ ུ ར ུ
Context Size 2:
ི ་ ས ྒ ྲ ོ ད [ ང ] པའ ི ་ དཀར ་ ཡ ི་ ས ླ ོ ང ་ ག ྱ ི ས ་ འབ ྱ ོ ན ་ བཅསན ་ ཆ ོ ས ་ རབ ་ འབ ྱ ུ ར ། ། ཁ ོ ངས
Context Size 3:
་ པ ་ ཆ ུ བ ་ བ ྱ ེ ད ། ། ཁ ྲ ་ བ ྱྱ ི ་ ཕ ་ ར ོ ལ ་ ར ླ བས ་ ཀ ྱ ི ་ རོ ད ་ ཀ ྱ ི ས ་ བད ུ ན ་ ཅ ི ་ མ ི ན
Context Size 4:
་ པའ ི ་ ར ྒ ྱ ར ་ བར ་ དཀའ ་ བའ ི ་ འཕ ྲ ུ་ ཀ ྱ ི ་ ནང ་ ག ི ་ འབ ུ མ ་ ཡང ་ ། ། ཤ་ ར ྒ ྱ ུ ད ་ པ ། ད ེ ་ ས ྟ ེ ། བ ྲ མ
Key Findings
- Best Predictability: Context-2 with 73.5% predictability
- Branching Factor: Decreases with context size (more deterministic)
- Memory Trade-off: Larger contexts require more storage (489,183 contexts)
- Recommendation: Context-3 or Context-4 for text generation
4. Vocabulary Analysis
Statistics
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Vocabulary Size | 13,016 |
| Total Tokens | 18,343,262 |
| Mean Frequency | 1409.29 |
| Median Frequency | 3 |
| Frequency Std Dev | 31347.07 |
Most Common Words
| Rank | Word | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ས | 1,859,452 |
| 2 | ར | 1,242,082 |
| 3 | ད | 1,225,016 |
| 4 | ན | 1,119,190 |
| 5 | ག | 979,844 |
| 6 | ལ | 962,286 |
| 7 | བ | 831,513 |
| 8 | ང | 704,629 |
| 9 | མ | 647,161 |
| 10 | པ | 638,483 |
Least Common Words (from vocabulary)
| Rank | Word | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ༡༡༦༠ | 2 |
| 2 | w1kg9520 | 2 |
| 3 | jayasena | 2 |
| 4 | ༡༡ཙམ | 2 |
| 5 | 252591 | 2 |
| 6 | 2525b4 | 2 |
| 7 | 2525b2 | 2 |
| 8 | caryā | 2 |
| 9 | gīti | 2 |
| 10 | caryāgītivṛtti | 2 |
Zipf's Law Analysis
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Zipf Coefficient | 1.8006 |
| R² (Goodness of Fit) | 0.975288 |
| Adherence Quality | excellent |
Coverage Analysis
| Top N Words | Coverage |
|---|---|
| Top 100 | 92.9% |
| Top 1,000 | 99.6% |
| Top 5,000 | 99.9% |
| Top 10,000 | 100.0% |
Key Findings
- Zipf Compliance: R²=0.9753 indicates excellent adherence to Zipf's law
- High Frequency Dominance: Top 100 words cover 92.9% of corpus
- Long Tail: 3,016 words needed for remaining 0.0% coverage
5. Word Embeddings Evaluation
Model Comparison
| Model | Vocab Size | Dimension | Avg Norm | Std Norm | Isotropy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mono_32d | 8,661 | 32 | 6.077 | 1.370 | 0.7739 🏆 |
| mono_64d | 8,661 | 64 | 6.426 | 1.018 | 0.7102 |
| mono_128d | 8,661 | 128 | 6.678 | 0.842 | 0.5344 |
| embeddings_enhanced | 0 | 0 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.0000 |
Key Findings
- Best Isotropy: mono_32d with 0.7739 (more uniform distribution)
- Dimension Trade-off: Higher dimensions capture more semantics but reduce isotropy
- Vocabulary Coverage: All models cover 8,661 words
- Recommendation: 100d for balanced semantic capture and efficiency
6. Summary & Recommendations
Production Recommendations
| Component | Recommended | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Tokenizer | 32k BPE | Best compression (5.96x) with low UNK rate |
| N-gram | 5-gram | Lowest perplexity (259) |
| Markov | Context-4 | Highest predictability (73.5%) |
| Embeddings | 100d | Balanced semantic capture and isotropy |
Appendix: Metrics Glossary & Interpretation Guide
This section provides definitions, intuitions, and guidance for interpreting the metrics used throughout this report.
Tokenizer Metrics
Compression Ratio
Definition: The ratio of characters to tokens (chars/token). Measures how efficiently the tokenizer represents text.
Intuition: Higher compression means fewer tokens needed to represent the same text, reducing sequence lengths for downstream models. A 3x compression means ~3 characters per token on average.
What to seek: Higher is generally better for efficiency, but extremely high compression may indicate overly aggressive merging that loses morphological information.
Average Token Length (Fertility)
Definition: Mean number of characters per token produced by the tokenizer.
Intuition: Reflects the granularity of tokenization. Longer tokens capture more context but may struggle with rare words; shorter tokens are more flexible but increase sequence length.
What to seek: Balance between 2-5 characters for most languages. Arabic/morphologically-rich languages may benefit from slightly longer tokens.
Unknown Token Rate (OOV Rate)
Definition: Percentage of tokens that map to the unknown/UNK token, indicating words the tokenizer cannot represent.
Intuition: Lower OOV means better vocabulary coverage. High OOV indicates the tokenizer encounters many unseen character sequences.
What to seek: Below 1% is excellent; below 5% is acceptable. BPE tokenizers typically achieve very low OOV due to subword fallback.
N-gram Model Metrics
Perplexity
Definition: Measures how "surprised" the model is by test data. Mathematically: 2^(cross-entropy). Lower values indicate better prediction.
Intuition: If perplexity is 100, the model is as uncertain as if choosing uniformly among 100 options at each step. A perplexity of 10 means effectively choosing among 10 equally likely options.
What to seek: Lower is better. Perplexity decreases with larger n-grams (more context). Values vary widely by language and corpus size.
Entropy
Definition: Average information content (in bits) needed to encode the next token given the context. Related to perplexity: perplexity = 2^entropy.
Intuition: High entropy means high uncertainty/randomness; low entropy means predictable patterns. Natural language typically has entropy between 1-4 bits per character.
What to seek: Lower entropy indicates more predictable text patterns. Entropy should decrease as n-gram size increases.
Coverage (Top-K)
Definition: Percentage of corpus occurrences explained by the top K most frequent n-grams.
Intuition: High coverage with few patterns indicates repetitive/formulaic text; low coverage suggests diverse vocabulary usage.
What to seek: Depends on use case. For language modeling, moderate coverage (40-60% with top-1000) is typical for natural text.
Markov Chain Metrics
Average Entropy
Definition: Mean entropy across all contexts, measuring average uncertainty in next-word prediction.
Intuition: Lower entropy means the model is more confident about what comes next. Context-1 has high entropy (many possible next words); Context-4 has low entropy (few likely continuations).
What to seek: Decreasing entropy with larger context sizes. Very low entropy (<0.1) indicates highly deterministic transitions.
Branching Factor
Definition: Average number of unique next tokens observed for each context.
Intuition: High branching = many possible continuations (flexible but uncertain); low branching = few options (predictable but potentially repetitive).
What to seek: Branching factor should decrease with context size. Values near 1.0 indicate nearly deterministic chains.
Predictability
Definition: Derived metric: (1 - normalized_entropy) × 100%. Indicates how deterministic the model's predictions are.
Intuition: 100% predictability means the next word is always certain; 0% means completely random. Real text falls between these extremes.
What to seek: Higher predictability for text generation quality, but too high (>98%) may produce repetitive output.
Vocabulary & Zipf's Law Metrics
Zipf's Coefficient
Definition: The slope of the log-log plot of word frequency vs. rank. Zipf's law predicts this should be approximately -1.
Intuition: A coefficient near -1 indicates the corpus follows natural language patterns where a few words are very common and most words are rare.
What to seek: Values between -0.8 and -1.2 indicate healthy natural language distribution. Deviations may suggest domain-specific or artificial text.
R² (Coefficient of Determination)
Definition: Measures how well the linear fit explains the frequency-rank relationship. Ranges from 0 to 1.
Intuition: R² near 1.0 means the data closely follows Zipf's law; lower values indicate deviation from expected word frequency patterns.
What to seek: R² > 0.95 is excellent; > 0.99 indicates near-perfect Zipf adherence typical of large natural corpora.
Vocabulary Coverage
Definition: Cumulative percentage of corpus tokens accounted for by the top N words.
Intuition: Shows how concentrated word usage is. If top-100 words cover 50% of text, the corpus relies heavily on common words.
What to seek: Top-100 covering 30-50% is typical. Higher coverage indicates more repetitive text; lower suggests richer vocabulary.
Word Embedding Metrics
Isotropy
Definition: Measures how uniformly distributed vectors are in the embedding space. Computed as the ratio of minimum to maximum singular values.
Intuition: High isotropy (near 1.0) means vectors spread evenly in all directions; low isotropy means vectors cluster in certain directions, reducing expressiveness.
What to seek: Higher isotropy generally indicates better-quality embeddings. Values > 0.1 are reasonable; > 0.3 is good. Lower-dimensional embeddings tend to have higher isotropy.
Average Norm
Definition: Mean magnitude (L2 norm) of word vectors in the embedding space.
Intuition: Indicates the typical "length" of vectors. Consistent norms suggest stable training; high variance may indicate some words are undertrained.
What to seek: Relatively consistent norms across models. The absolute value matters less than consistency (low std deviation).
Cosine Similarity
Definition: Measures angular similarity between vectors, ranging from -1 (opposite) to 1 (identical direction).
Intuition: Words with similar meanings should have high cosine similarity. This is the standard metric for semantic relatedness in embeddings.
What to seek: Semantically related words should score > 0.5; unrelated words should be near 0. Synonyms often score > 0.7.
t-SNE Visualization
Definition: t-Distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding - a dimensionality reduction technique that preserves local structure for visualization.
Intuition: Clusters in t-SNE plots indicate groups of semantically related words. Spread indicates vocabulary diversity; tight clusters suggest semantic coherence.
What to seek: Meaningful clusters (e.g., numbers together, verbs together). Avoid over-interpreting distances - t-SNE preserves local, not global, structure.
General Interpretation Guidelines
- Compare within model families: Metrics are most meaningful when comparing models of the same type (e.g., 8k vs 64k tokenizer).
- Consider trade-offs: Better performance on one metric often comes at the cost of another (e.g., compression vs. OOV rate).
- Context matters: Optimal values depend on downstream tasks. Text generation may prioritize different metrics than classification.
- Corpus influence: All metrics are influenced by corpus characteristics. Wikipedia text differs from social media or literature.
- Language-specific patterns: Morphologically rich languages (like Arabic) may show different optimal ranges than analytic languages.
Visualizations Index
| Visualization | Description |
|---|---|
| Tokenizer Compression | Compression ratios by vocabulary size |
| Tokenizer Fertility | Average token length by vocabulary |
| Tokenizer OOV | Unknown token rates |
| Tokenizer Total Tokens | Total tokens by vocabulary |
| N-gram Perplexity | Perplexity by n-gram size |
| N-gram Entropy | Entropy by n-gram size |
| N-gram Coverage | Top pattern coverage |
| N-gram Unique | Unique n-gram counts |
| Markov Entropy | Entropy by context size |
| Markov Branching | Branching factor by context |
| Markov Contexts | Unique context counts |
| Zipf's Law | Frequency-rank distribution with fit |
| Vocab Frequency | Word frequency distribution |
| Top 20 Words | Most frequent words |
| Vocab Coverage | Cumulative coverage curve |
| Embedding Isotropy | Vector space uniformity |
| Embedding Norms | Vector magnitude distribution |
| Embedding Similarity | Word similarity heatmap |
| Nearest Neighbors | Similar words for key terms |
| t-SNE Words | 2D word embedding visualization |
| t-SNE Sentences | 2D sentence embedding visualization |
| Position Encoding | Encoding method comparison |
| Model Sizes | Storage requirements |
| Performance Dashboard | Comprehensive performance overview |
About This Project
Data Source
Models trained on wikipedia-monthly - a monthly snapshot of Wikipedia articles across 300+ languages.
Project
A project by Wikilangs - Open-source NLP models for every Wikipedia language.
Maintainer
Citation
If you use these models in your research, please cite:
@misc{wikilangs2025,
author = {Kamali, Omar},
title = {Wikilangs: Open NLP Models for Wikipedia Languages},
year = {2025},
publisher = {HuggingFace},
url = {https://huggingface.co/wikilangs}
institution = {Omneity Labs}
}
License
MIT License - Free for academic and commercial use.
Links
- 🌐 Website: wikilangs.org
- 🤗 Models: huggingface.co/wikilangs
- 📊 Data: wikipedia-monthly
- 👤 Author: Omar Kamali
Generated by Wikilangs Models Pipeline
Report Date: 2025-12-28 07:45:49